COURSE INFORMATION
The Level 7 Diploma in Strategic Health & Safety Management and Leadership qualification is aimed at candidates who are responsible for developing and applying health and safety procedures day-to-day in any organisation. They are likely to be managers looking to improve their knowledge and skills.
The awarding body for this qualification is ProQual Awarding Body and the regulatory body is the Office of Qualifications and Examinations Regulation (Ofqual). This qualification has been accredited onto the Regulated Qualifications Framework (RQF).


ENTRY REQUIREMENTS
Candidates must have good command of English language(reading & writing)
QUALIFICATION STRUCTURE
WHAT’S INCLUDED:
- instructor
- Training equipment
- Exams
- Awards
- Classroom
- Range (where applicable)
- Ammo (where applicable)
WHAT IS NOT INCLUDED:
- Accommodation (where applicable)
- Food and beverages
- Flights (where applicable)
- Airport Transfers (where applicable)
- Safety Glasses (where applicable)
- Ear Defenders (where applicable)
Course Length
Course Cost
£1800
Location
UK, Europe, USA, and Thailand
Course Dates
Any time of the month
Award
ProQual Level 7 Diploma in Strategic Health and Safety Leadership and Management
Assessments
There must be valid, authentic and sufficient for all the assessment criteria. However, one piece of evidence may be used to meet the requirements of more than one learning outcome or assessment criterion.
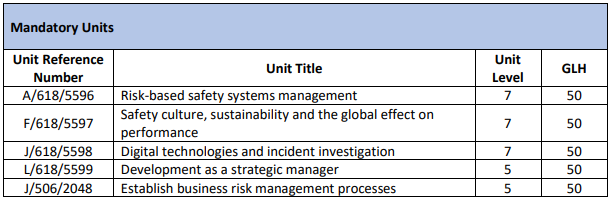
QUALIFICATION STRUCTURE
Unit A/618/5596
RISK-BASED SAFETY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
Learning Outcome – The learner will: | Assessment Criterion – The learner can:
1. Be able to develop and implement current ISO standards for occupational health and safety
1.1 Evaluate the extent to which the processes of an occupational health and safety management system links to any ISO clauses
1.2 Analyse any gaps to be bridged to satisfy the requirements of an ISO occupational health and safety management system
1.3 Evaluate the issues/challenges faced by an organisation while implementing an ISO compliant, or other recognised, occupational health and safety management system
1.4 Evaluate the importance of understanding the organisation and its context whilst framing occupational health and management systems
1.5 Analyse the external and internal issues have an impact on the way an organisation manages its occupational health and safety management system responsibilities
1.6 Assess the way in which the activities of subcontractors and third parties might have a negative impact on an organisation’s occupational health and safety systems
1.7 Differentiate between the various recognised occupational health and safety standards
1.8 Ensure the alignment of the occupational health and safety management system with an organisation’s strategic goals and that it meets legal, regulatory and compliance requirements.
2. Be able to evaluate strategic risks to an organisation through the implementation of a quantifiable risk assessment system
2.1 Evaluate the role of suitable leadership and management in the organisation risk reduction system(s)
2.2 Analyse the value of accident causation in managing the impact of risk(s) identified
2.3 Analyse the requirements of performing fault tree and event tree analysis to show fact based decisions
2.4 Analyse the relevance, validity and value of different data sources and information to implement a quantified risk assessment model
2.5 Evaluate the internal and external factors influencing the selection of different risk quantification models
2.6 Develop practicable action plans that improve controls to reduce strategic risks and present them at director board level
2.7 Develop practicable strategies on the ways in which an organisation can assess hazards and risks following changes in an organisation’s management, processes and or equipment
2.8 Analyse the pitfalls in any risk transfer
2.9 Analyse the different types and categories of strategic and dynamic risks
3. Be able to articulate risk communication strategies in various situations
3.1 Develop practicable strategies for risk communication for a range of situations that take stakeholders’ requirements and legal requirements into consideration
3.2 Assign ownership and accountabilities and gain agreement from managers/directors and the workforce for strategic and dynamic risks
3.3 Evaluate the importance of effective communication and consultation in a risk management process
3.4 Analyse the way in which a crisis communication could differ from a risk communication
Unit A/618/5596
RISK-BASED SAFETY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
Learning Outcome – The learner will: | Assessment Criterion – The learner can:
1. Be able to evaluate the effects of global issues on safety culture
1.1 Evaluate the impact of globalisation on the safety climate of an organisation
1.2 Analyse the way in which perceptions of safety and unsafe behaviour vary between various countries
1.3 Evaluate the role of management in ensuring the development of a worker’s competence within their role
1.4 Develop practicable and operational plans for the effective management of occupational health and safety in a multi-employer worksite
1.5 Analyse the way in which Globally Harmonised Systems could improve the communication of hazards and risk
2. Evaluate the benefits of sustainability in the workplace
2.1 Develop a business case for the inclusion of occupational health and safety in sustainability strategies
2.2 Evaluate the challenges, opportunities and strategic business benefits in promoting sustainable workplace health and safety
2.3 Specify the methods to be included that measure a sustainable occupational health and safety practice in workplaces
3. Be able to measure safety performance and calculate safety return on any investment
3.1 Analyse the way in which error management can improve the safety performance in occupational health and safety management systems
3.2 Develop a practicable model for calculating any returns on the occupational health and safety management system in operational and strategic terms
3.3 Develop a data evidence method that measures the performance of the safety culture
4. Understand the effects of psychological health and injury management in the workplace
4.1 Evaluate the role of management in promoting good mental health within the workplace
4.2 Analyse the challenges in dealing with mental health within the workplace
4.3 Analyse the way in which the human rights of workers with mental health conditions should be protected in the workplace
4.4 Analyse the factors and conditions contributing to possible workplace violence
4.5 Analyse the early indicators of workplace confrontation
4.6 Analyse the barriers to the implementation of a psychological health and safety management system in the workplace
4.7 Analyse the ways in which an injury management programme can have an impact on a worker’s morale
4.8 Evaluate the potential costs of poor psychological and physical health and poor morale can have on an organisation
5. Be able to lead the implementation of a whole-organisation approach to occupational health and safety
5.1 Evaluate the case for the integration of occupational health and safety into an organisation’s business activity
5.2 Develop a practicable whole-organisation approach to occupational health and safety in an organisation
5.3 Analyse the relevance of a whole-organisation approach in tackling bullying and violence
5.4 Scope the nature of interdependence in the components of an occupational health and safety system
5.5 Develop a strategic response and operational plans that address aggregated, interdependent health and safety risks
Unit J/618/5598
DIGITAL TECHNOLOGIES AND INCIDENT INVESTIGATION
Learning Outcome – The learner will: | Assessment Criterion – The learner can:
1. Understand the effects of digital technologies on strategic and operational occupational health and safety management
1.1 Evaluate the impact of digital technology on occupational health and safety within an organisation
1.2 Analyse the ways in which advanced robotics and artificial intelligence could contribute to the improved reduction of risks
1.3 Analyse the way in which advanced robotics and artificial intelligence could be detrimental to workers’ mental health longer term and develop a response that addresses these highlighted risks
2. Be able to implement a biohazards risk assessment and control measures in the workplace
2.1 Analyse the way in which exposure and assessment are used in risk management
2.2 Analyse the way in which different workplaces can be protected from various identifiable infections
2.3 Develop a strategy that can reduce/limit the spread of infection within different workplaces
2.4 Analyse the requirements of a risk communication strategy to prevent the spread of infection
3. Understand the implementation of ecological risk assessment and control measures
3.1 Analyse the way in which the strategic and management goals of an organisation may be met whilst addressing the impact of industrial activities on an ecosystem
3.2 Develop a realistic risk identification for an organisation’s ecological activities
3.3 Quantify an assessment for an organisation’s industrial activities
3.4 Evaluate the strategic and operational requirements of an ecological risk assessment that assesses the risks posed by industrial effluent on downstream ecosystems
4. Be able to implement engineering solutions for ergonomic hazards and control measures
4.1 Analyse the ergonomic risk factors in the workplace and their strategic and operational implications
4.2 Develop practicable ergonomic solutions that address risks in the workplace and their strategic and operational implications
4.3 Quantify the costs and benefits of ergonomic solutions in the workplace
5. Understand the requirements of the implementation of risk assessment for biological outbreaks and control measures
5.1 Analyse the requirements of strategic risk and risk assessment for biological outbreaks
5.2 Analyse the requirements of immediate, mid and long term effective control measures to be implemented
5.3 Analyse the factors to be considered for a postdisaster assessment and reviews
6. Understand the likely failure scenarios for chemical hazards and control measures
6.1 Analyse the safety management requirements of process areas and identify likely failure points
6.2 Analyse the suitability and sufficiency of control measures for a process area and develop plans for improvement
7. Be able to implement an accident causal analysis model for physical hazards
7.1 Identify the case of an accident through the application of root cause analysis
7.2 Develop practicable plans for the avoidance of similar accidents
7.3 Assess the costs to an organisation of physical accidents (financial, loss of time, reputational damage, complaints and general worker welfare issues)
7.4 Quantify the benefits of any enhanced safety control measures
Unit L/618/5599
DEVELOPMENT AS A STRATEGIC MANAGER
Learning Outcome – The learner will: | Assessment Criterion – The learner can:
1. Be able to identify personal skills to achieve strategic ambitions
1.1 Critically analyse the strategic direction of the organisation and where they fit it
1.2 Critically evaluate the strategic skills required of a leader/manager operating in a complex environment to achieve personal and organisational strategic ambitions
1.3 Assess the relationship between existing and proposed future skills to achieve strategic ambitions
2. Be able to manage personal leadership/management development to support achievement of strategic organisation and personal ambitions
2.1 Critically discuss the opportunities to support their leadership/management development
2.2 Design a personal development plan to direct leadership/management development in a complex environment
2.3 Devise and agree an implementation process to ensure the success of the development plan that can realise substantial changes in their leadership/management style
3. Be able to evaluate the effectiveness of the leadership/management development plan
3.1 Critically evaluate the achievement of outcomes of the plan against the original agreed objectives
3.2 Evaluate the impact of leadership/management style and the achievement of objectives on strategic ambitions in different organisational settings
3.3 Critically review and update the leadership/management development plan
4. Be able to advocate an employee welfare environment that supports organisational values
4.1 Critically evaluate the impact of the corporate commitment to employee welfare on strategic objectives
4.2 Discuss how an employee welfare environment can affect achievement of strategic organisational objectives
4.3 Determine the influence of corporate commitment to employee welfare on the development of organisational values that will realist strategic ambitions
5. Be able to maintain and record their professional development
5.1 Maintain a personal development portfolio which can contribute to professional bodies’ CPD requirements and which incorporates:
• An ongoing evaluation of their personal competence
• Reflective commentaries on CPD activities
• Setting and prioritising realistic goals for professional development
• Applying professional ethics in practice
• An appreciation of diversity and inclusivity in workplaces
• Sharing personal experiences in professional debate and discussion
Unit J/506/2048
ESTABLISH BUSINESS RISK MANAGEMENT PROCESSES
Learning Outcome – The learner will: | Assessment Criterion – The learner can:
1. Understand business risk management models and techniques
1.1 Analyse standards relating to the management of business risk
1.2 Analyse the factors influencing different types of risk
1.3 Evaluate the relationship between risk management, business continuity and crisis management
1.4 Evaluate a range of scenario planning and crisis management models
1.5 Analyse methods of calculating risk probability
1.6 Analyse the effectiveness of a range of risk monitoring techniques
1.7 Analyse the significance of risk governance structures and ownership
2. Be able to develop business risk management processes
2.1 Review periodically the effectiveness of risk management strategy, policy and criteria
2.2 Take action to ensure that risk profiles remain current and relevant
2.3 Develop viable and affordable risk management processes that are consistent with business needs and the degree of potential impact of the risk
2.4 Develop contingency and business disruption processes that are commensurate with the degree of risk to business as usual and organisational reputation
2.5 Take action to ensure that risk management processes are integrated into operational plans and activities
3. Be able to evaluate the effectiveness of business risk management process
3.1 Appraise the suitability of a range of risk evaluation techniques to business risk management
3.2 Evaluate risk using valid quantitative and qualitative information
3.3 Identify areas for improvement in identifying and managing risk
3.4 Encourage a culture that accepts and manages risk













